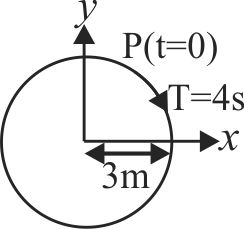
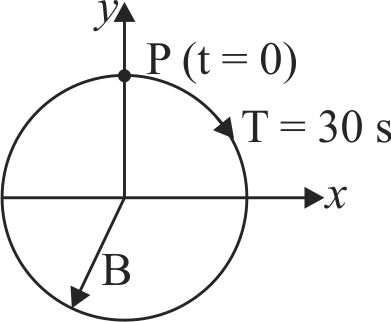
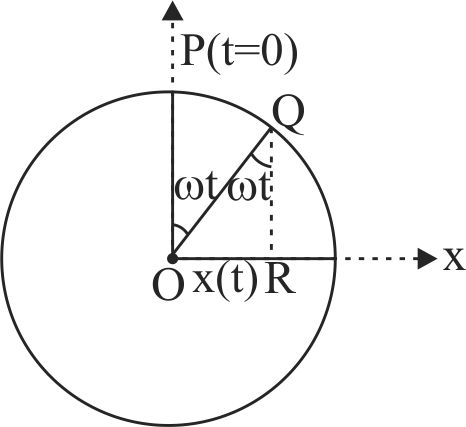
364236 An object of mass \(m\) is moving in a uniform circular motion in the \(xy\) plane. The circle has radius \(R\) and the object is moving around the circle with speed \(v\). The motion is projected onto the \(x\)-axis where it appears as simple harmonic motion according to \(x(t) = R\cos (\omega t + \phi )\). Here \(\omega\) is equal to
364236 An object of mass \(m\) is moving in a uniform circular motion in the \(xy\) plane. The circle has radius \(R\) and the object is moving around the circle with speed \(v\). The motion is projected onto the \(x\)-axis where it appears as simple harmonic motion according to \(x(t) = R\cos (\omega t + \phi )\). Here \(\omega\) is equal to
364236 An object of mass \(m\) is moving in a uniform circular motion in the \(xy\) plane. The circle has radius \(R\) and the object is moving around the circle with speed \(v\). The motion is projected onto the \(x\)-axis where it appears as simple harmonic motion according to \(x(t) = R\cos (\omega t + \phi )\). Here \(\omega\) is equal to
364236 An object of mass \(m\) is moving in a uniform circular motion in the \(xy\) plane. The circle has radius \(R\) and the object is moving around the circle with speed \(v\). The motion is projected onto the \(x\)-axis where it appears as simple harmonic motion according to \(x(t) = R\cos (\omega t + \phi )\). Here \(\omega\) is equal to