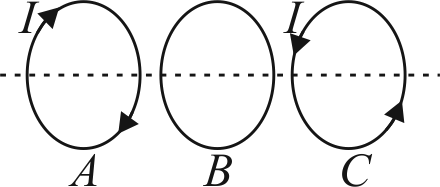358672
Three identical coils \(A\), \(B\) and \(C\) carrying currents are placed coaxially with their planes parallel to one another. \(A\) and \(C\) carry current as shown in figure \(B\) is kept fixed while \(A\) and \(C\) both are moved towards \(B\) with the same speed. Initially, \(B\) is equally separated from \(A\) and \(C\). The direction of the induced current in the coil \(B\) is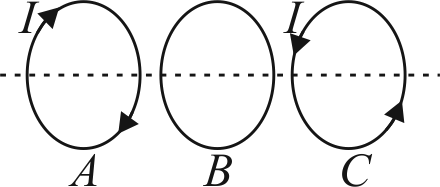
358672
Three identical coils \(A\), \(B\) and \(C\) carrying currents are placed coaxially with their planes parallel to one another. \(A\) and \(C\) carry current as shown in figure \(B\) is kept fixed while \(A\) and \(C\) both are moved towards \(B\) with the same speed. Initially, \(B\) is equally separated from \(A\) and \(C\). The direction of the induced current in the coil \(B\) is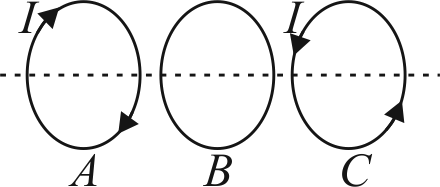
358672
Three identical coils \(A\), \(B\) and \(C\) carrying currents are placed coaxially with their planes parallel to one another. \(A\) and \(C\) carry current as shown in figure \(B\) is kept fixed while \(A\) and \(C\) both are moved towards \(B\) with the same speed. Initially, \(B\) is equally separated from \(A\) and \(C\). The direction of the induced current in the coil \(B\) is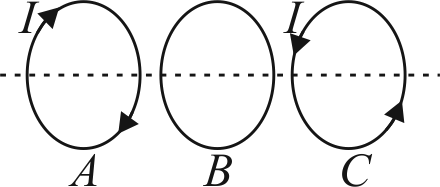
358672
Three identical coils \(A\), \(B\) and \(C\) carrying currents are placed coaxially with their planes parallel to one another. \(A\) and \(C\) carry current as shown in figure \(B\) is kept fixed while \(A\) and \(C\) both are moved towards \(B\) with the same speed. Initially, \(B\) is equally separated from \(A\) and \(C\). The direction of the induced current in the coil \(B\) is