358376
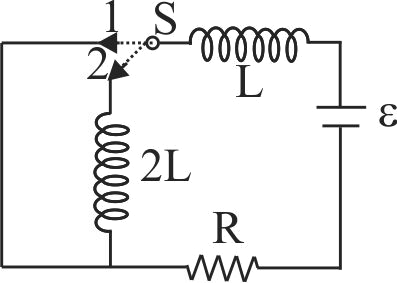
In the circuit shown here, the point ' \(C\) ' is kept connected to point ' \(A\) ' till the current flowing through the circuit becomes constant. Afterward, suddenly, point ' \(C\) ' is disconnected from point ' \(A\) ' and connected to point ' \(B\) ' at time \(t = 0\). Ratio of the voltage across resistance and the inductor at \(t = L/R\) will be equal to:
358376
In the circuit shown here, the point ' \(C\) ' is kept connected to point ' \(A\) ' till the current flowing through the circuit becomes constant. Afterward, suddenly, point ' \(C\) ' is disconnected from point ' \(A\) ' and connected to point ' \(B\) ' at time \(t = 0\). Ratio of the voltage across resistance and the inductor at \(t = L/R\) will be equal to:
358376
In the circuit shown here, the point ' \(C\) ' is kept connected to point ' \(A\) ' till the current flowing through the circuit becomes constant. Afterward, suddenly, point ' \(C\) ' is disconnected from point ' \(A\) ' and connected to point ' \(B\) ' at time \(t = 0\). Ratio of the voltage across resistance and the inductor at \(t = L/R\) will be equal to:
358376
In the circuit shown here, the point ' \(C\) ' is kept connected to point ' \(A\) ' till the current flowing through the circuit becomes constant. Afterward, suddenly, point ' \(C\) ' is disconnected from point ' \(A\) ' and connected to point ' \(B\) ' at time \(t = 0\). Ratio of the voltage across resistance and the inductor at \(t = L/R\) will be equal to: