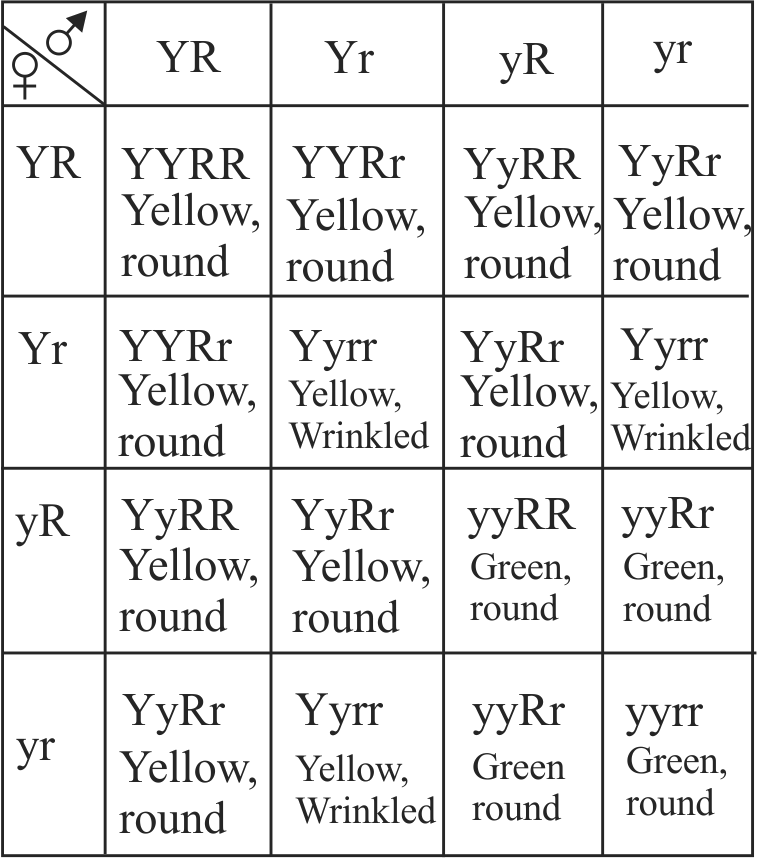
342293 Three yellow and round pea seeds labelled A,B,C were taken and grown into plants. The plants were crossed to a plant grown from green wrinkled pea. 100 seeds obtained from each cross were sorted into phenotypic classes as follows: A: 100 yellow round, B: 51 yellow round 49 green round, \(\mathrm{C}: 24\) yellow round, 26 yellow wrinkled, 25 green round, 25 green wrinkled. The genotype of plant \(C\) would be
342293 Three yellow and round pea seeds labelled A,B,C were taken and grown into plants. The plants were crossed to a plant grown from green wrinkled pea. 100 seeds obtained from each cross were sorted into phenotypic classes as follows: A: 100 yellow round, B: 51 yellow round 49 green round, \(\mathrm{C}: 24\) yellow round, 26 yellow wrinkled, 25 green round, 25 green wrinkled. The genotype of plant \(C\) would be
342293 Three yellow and round pea seeds labelled A,B,C were taken and grown into plants. The plants were crossed to a plant grown from green wrinkled pea. 100 seeds obtained from each cross were sorted into phenotypic classes as follows: A: 100 yellow round, B: 51 yellow round 49 green round, \(\mathrm{C}: 24\) yellow round, 26 yellow wrinkled, 25 green round, 25 green wrinkled. The genotype of plant \(C\) would be
342293 Three yellow and round pea seeds labelled A,B,C were taken and grown into plants. The plants were crossed to a plant grown from green wrinkled pea. 100 seeds obtained from each cross were sorted into phenotypic classes as follows: A: 100 yellow round, B: 51 yellow round 49 green round, \(\mathrm{C}: 24\) yellow round, 26 yellow wrinkled, 25 green round, 25 green wrinkled. The genotype of plant \(C\) would be
342293 Three yellow and round pea seeds labelled A,B,C were taken and grown into plants. The plants were crossed to a plant grown from green wrinkled pea. 100 seeds obtained from each cross were sorted into phenotypic classes as follows: A: 100 yellow round, B: 51 yellow round 49 green round, \(\mathrm{C}: 24\) yellow round, 26 yellow wrinkled, 25 green round, 25 green wrinkled. The genotype of plant \(C\) would be