338986
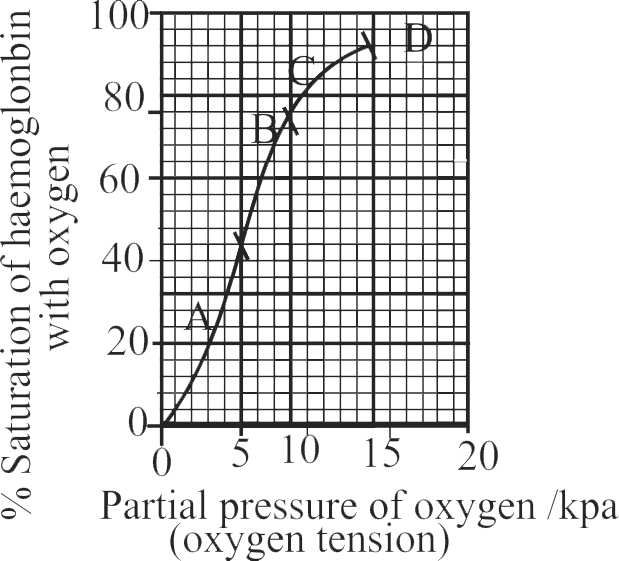
Statement A :
In the alveoli, there is high \(\mathrm{pO}_{2}\), low \(\mathrm{pCO}_{2}\), lesser \(\mathrm{H}^{+}\) concentration and higher temperature, the factors are all favourable for the formation of oxyhaemoglobin
Statement B :
In the tissues, where low \(\mathrm{pO}_{2}\), high \(\mathrm{pCO}_{2}\), high \(\mathrm{H}^{+}\) concentration and higher temperature exist, it results in dissociation of oxygen from the oxyhaemoglobin.
338986
Statement A :
In the alveoli, there is high \(\mathrm{pO}_{2}\), low \(\mathrm{pCO}_{2}\), lesser \(\mathrm{H}^{+}\) concentration and higher temperature, the factors are all favourable for the formation of oxyhaemoglobin
Statement B :
In the tissues, where low \(\mathrm{pO}_{2}\), high \(\mathrm{pCO}_{2}\), high \(\mathrm{H}^{+}\) concentration and higher temperature exist, it results in dissociation of oxygen from the oxyhaemoglobin.
338986
Statement A :
In the alveoli, there is high \(\mathrm{pO}_{2}\), low \(\mathrm{pCO}_{2}\), lesser \(\mathrm{H}^{+}\) concentration and higher temperature, the factors are all favourable for the formation of oxyhaemoglobin
Statement B :
In the tissues, where low \(\mathrm{pO}_{2}\), high \(\mathrm{pCO}_{2}\), high \(\mathrm{H}^{+}\) concentration and higher temperature exist, it results in dissociation of oxygen from the oxyhaemoglobin.
338986
Statement A :
In the alveoli, there is high \(\mathrm{pO}_{2}\), low \(\mathrm{pCO}_{2}\), lesser \(\mathrm{H}^{+}\) concentration and higher temperature, the factors are all favourable for the formation of oxyhaemoglobin
Statement B :
In the tissues, where low \(\mathrm{pO}_{2}\), high \(\mathrm{pCO}_{2}\), high \(\mathrm{H}^{+}\) concentration and higher temperature exist, it results in dissociation of oxygen from the oxyhaemoglobin.