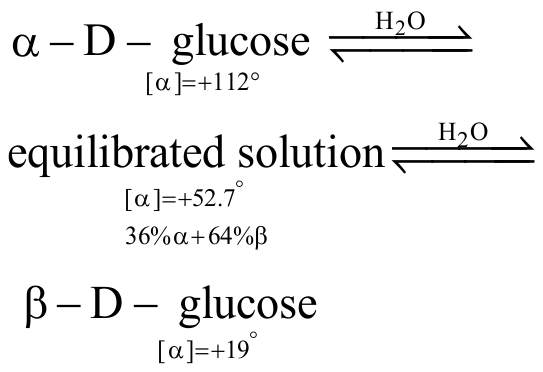
324629 Optical rotation of a freshly prepared solution of \(\mathrm{\alpha}\)-D-glucopyranose is \(\mathrm{+111^{\circ}}\) while that of \(\mathrm{\beta}\) - D-glucopyranose is \(\mathrm{+19.2^{\circ}}\). In solution, an equilibrium mixture of these two anomers is \(\mathrm{52.5^{\circ}}\). The percentage of \(\mathrm{\alpha}\)-form in the equilibrium mixture is
324629 Optical rotation of a freshly prepared solution of \(\mathrm{\alpha}\)-D-glucopyranose is \(\mathrm{+111^{\circ}}\) while that of \(\mathrm{\beta}\) - D-glucopyranose is \(\mathrm{+19.2^{\circ}}\). In solution, an equilibrium mixture of these two anomers is \(\mathrm{52.5^{\circ}}\). The percentage of \(\mathrm{\alpha}\)-form in the equilibrium mixture is
324629 Optical rotation of a freshly prepared solution of \(\mathrm{\alpha}\)-D-glucopyranose is \(\mathrm{+111^{\circ}}\) while that of \(\mathrm{\beta}\) - D-glucopyranose is \(\mathrm{+19.2^{\circ}}\). In solution, an equilibrium mixture of these two anomers is \(\mathrm{52.5^{\circ}}\). The percentage of \(\mathrm{\alpha}\)-form in the equilibrium mixture is
324629 Optical rotation of a freshly prepared solution of \(\mathrm{\alpha}\)-D-glucopyranose is \(\mathrm{+111^{\circ}}\) while that of \(\mathrm{\beta}\) - D-glucopyranose is \(\mathrm{+19.2^{\circ}}\). In solution, an equilibrium mixture of these two anomers is \(\mathrm{52.5^{\circ}}\). The percentage of \(\mathrm{\alpha}\)-form in the equilibrium mixture is