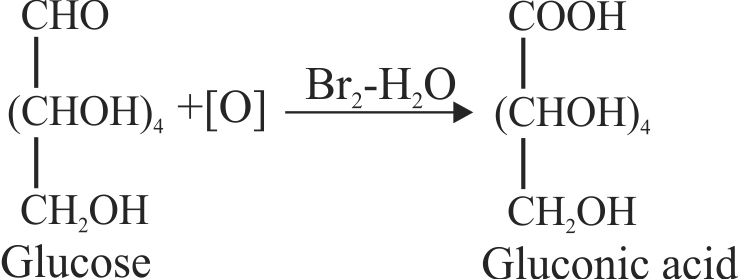324670
Which of the following properties of glucose cannot be explained by its open chain structure?
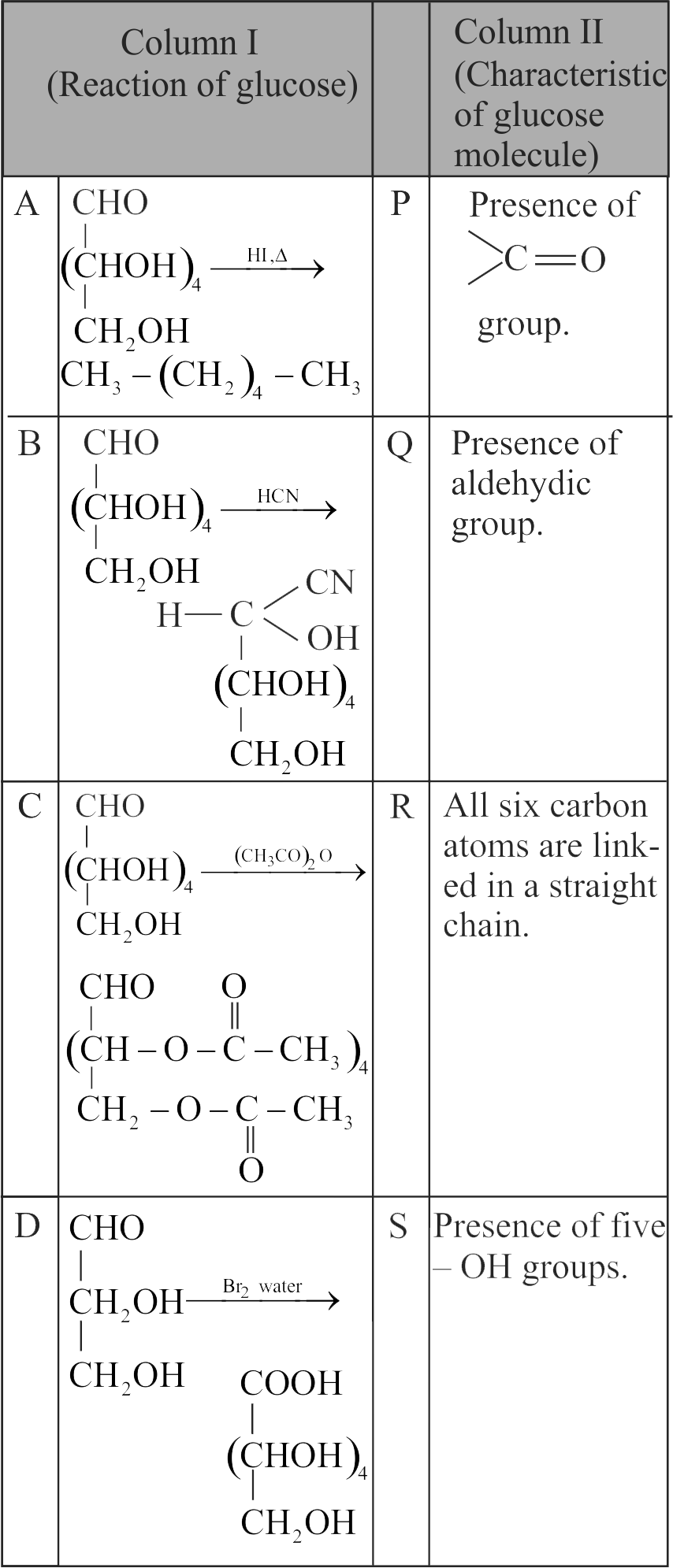
(i) Glucose does not form hydrogen sulphite with \(\mathrm{\mathrm{NaHSO}_{3}}\)
(ii) On oxidation with \(\mathrm{\mathrm{HNO}_{3}}\) glucose gives saccharic acid.
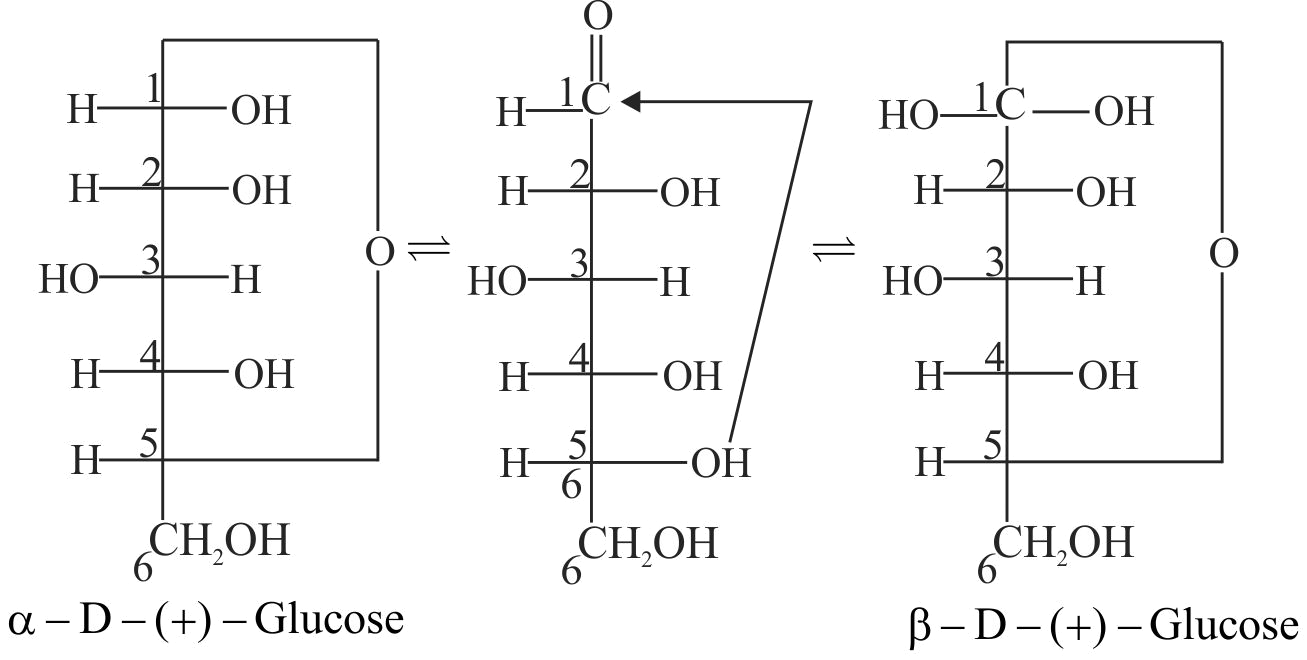
(iii) Glucose is found to exist in two different crystalline forms which are named as \(\mathrm{\alpha}\) and \(\mathrm{\beta}\).
324670
Which of the following properties of glucose cannot be explained by its open chain structure?
(i) Glucose does not form hydrogen sulphite with \(\mathrm{\mathrm{NaHSO}_{3}}\)
(ii) On oxidation with \(\mathrm{\mathrm{HNO}_{3}}\) glucose gives saccharic acid.
(iii) Glucose is found to exist in two different crystalline forms which are named as \(\mathrm{\alpha}\) and \(\mathrm{\beta}\).
324670
Which of the following properties of glucose cannot be explained by its open chain structure?
(i) Glucose does not form hydrogen sulphite with \(\mathrm{\mathrm{NaHSO}_{3}}\)
(ii) On oxidation with \(\mathrm{\mathrm{HNO}_{3}}\) glucose gives saccharic acid.
(iii) Glucose is found to exist in two different crystalline forms which are named as \(\mathrm{\alpha}\) and \(\mathrm{\beta}\).
324670
Which of the following properties of glucose cannot be explained by its open chain structure?
(i) Glucose does not form hydrogen sulphite with \(\mathrm{\mathrm{NaHSO}_{3}}\)
(ii) On oxidation with \(\mathrm{\mathrm{HNO}_{3}}\) glucose gives saccharic acid.
(iii) Glucose is found to exist in two different crystalline forms which are named as \(\mathrm{\alpha}\) and \(\mathrm{\beta}\).
324670
Which of the following properties of glucose cannot be explained by its open chain structure?
(i) Glucose does not form hydrogen sulphite with \(\mathrm{\mathrm{NaHSO}_{3}}\)
(ii) On oxidation with \(\mathrm{\mathrm{HNO}_{3}}\) glucose gives saccharic acid.
(iii) Glucose is found to exist in two different crystalline forms which are named as \(\mathrm{\alpha}\) and \(\mathrm{\beta}\).