323791
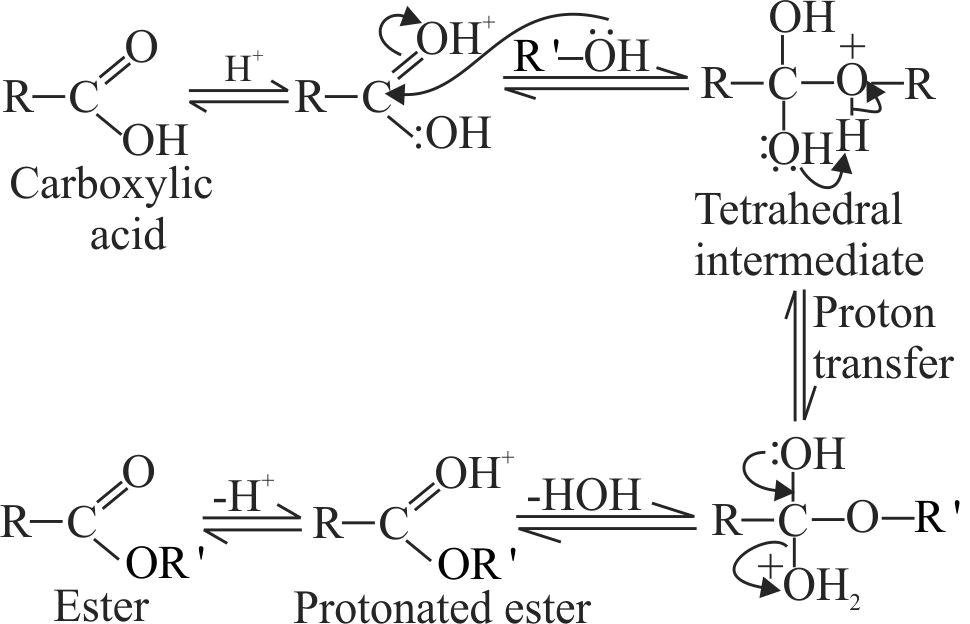
The following steps are given for the mechanism of esterification of carboxylic acids.
I. The protonated esters looses a proton to give the ester.
II. Protonation of the carbonyl oxygen activates the carbonyl group towards nucleophilic addition of the alcohol.
III. Proton transfer in the tetrahedral intermediate occurs.
Arrange the following steps in their correct sequence.
323791
The following steps are given for the mechanism of esterification of carboxylic acids.
I. The protonated esters looses a proton to give the ester.
II. Protonation of the carbonyl oxygen activates the carbonyl group towards nucleophilic addition of the alcohol.
III. Proton transfer in the tetrahedral intermediate occurs.
Arrange the following steps in their correct sequence.
323791
The following steps are given for the mechanism of esterification of carboxylic acids.
I. The protonated esters looses a proton to give the ester.
II. Protonation of the carbonyl oxygen activates the carbonyl group towards nucleophilic addition of the alcohol.
III. Proton transfer in the tetrahedral intermediate occurs.
Arrange the following steps in their correct sequence.
323791
The following steps are given for the mechanism of esterification of carboxylic acids.
I. The protonated esters looses a proton to give the ester.
II. Protonation of the carbonyl oxygen activates the carbonyl group towards nucleophilic addition of the alcohol.
III. Proton transfer in the tetrahedral intermediate occurs.
Arrange the following steps in their correct sequence.