321928
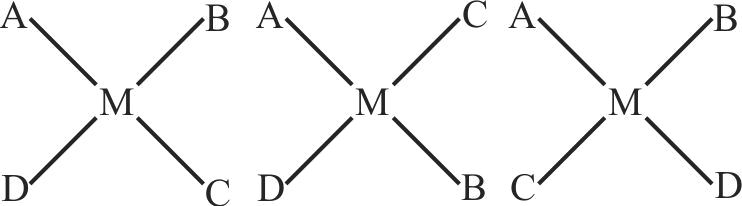
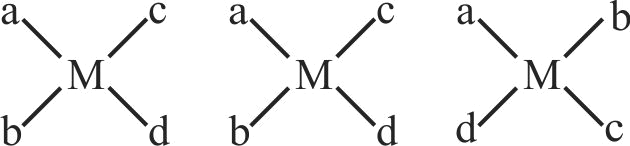
The number of geometrical isomers possible for a square planar complex of the type \({\left[ {{\rm{Mabcd}}} \right]^{{\rm{n \pm }}}}\) is ' \({\mathrm{x}}\) '. The number of geometrical isomers possible for octahedral complex of the type \({\left[ {{\rm{M}}{{\rm{a}}_{\rm{4}}}{{\rm{b}}_{\rm{2}}}} \right]^{{\rm{n}} \pm }}\) is
' \({\mathrm{y}}\) '. Sum of \({\mathrm{x}}\) and \({\mathrm{y}}\) is ____. (a,b, c, d are monodentate ligands)
321928
The number of geometrical isomers possible for a square planar complex of the type \({\left[ {{\rm{Mabcd}}} \right]^{{\rm{n \pm }}}}\) is ' \({\mathrm{x}}\) '. The number of geometrical isomers possible for octahedral complex of the type \({\left[ {{\rm{M}}{{\rm{a}}_{\rm{4}}}{{\rm{b}}_{\rm{2}}}} \right]^{{\rm{n}} \pm }}\) is
' \({\mathrm{y}}\) '. Sum of \({\mathrm{x}}\) and \({\mathrm{y}}\) is ____. (a,b, c, d are monodentate ligands)
321928
The number of geometrical isomers possible for a square planar complex of the type \({\left[ {{\rm{Mabcd}}} \right]^{{\rm{n \pm }}}}\) is ' \({\mathrm{x}}\) '. The number of geometrical isomers possible for octahedral complex of the type \({\left[ {{\rm{M}}{{\rm{a}}_{\rm{4}}}{{\rm{b}}_{\rm{2}}}} \right]^{{\rm{n}} \pm }}\) is
' \({\mathrm{y}}\) '. Sum of \({\mathrm{x}}\) and \({\mathrm{y}}\) is ____. (a,b, c, d are monodentate ligands)
321928
The number of geometrical isomers possible for a square planar complex of the type \({\left[ {{\rm{Mabcd}}} \right]^{{\rm{n \pm }}}}\) is ' \({\mathrm{x}}\) '. The number of geometrical isomers possible for octahedral complex of the type \({\left[ {{\rm{M}}{{\rm{a}}_{\rm{4}}}{{\rm{b}}_{\rm{2}}}} \right]^{{\rm{n}} \pm }}\) is
' \({\mathrm{y}}\) '. Sum of \({\mathrm{x}}\) and \({\mathrm{y}}\) is ____. (a,b, c, d are monodentate ligands)