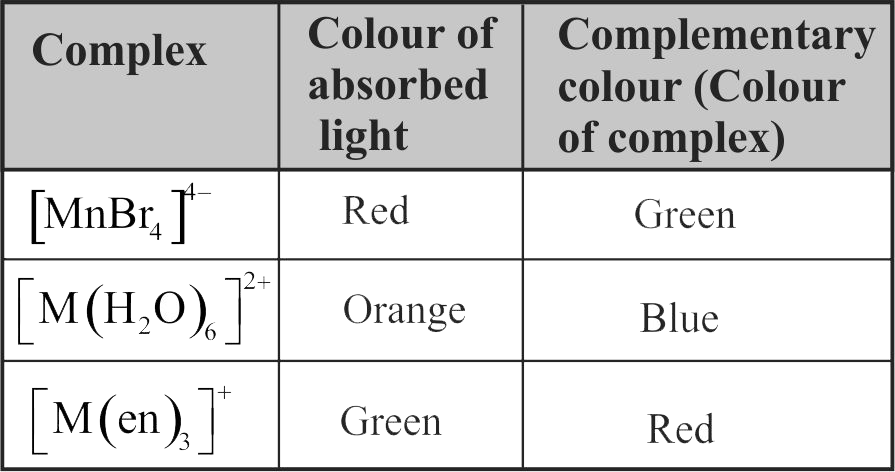
321794 An ion \({{\text{M}}^{{\text{2 + }}}}\), form the complexes \({\left[ {{\text{M}}{{\left( {{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}} \right)}_{\text{6}}}} \right]^{{\text{2 + }}}}{\text{,}}{\left[ {{\text{M(en}}{{\text{)}}_{\text{3}}}} \right]^{{\text{2 + }}}}\) and \({\left[ {{\text{MB}}{{\text{r}}_{\text{6}}}} \right]^{{\text{4 - }}}}\) Colour of these complexes may be:
321794 An ion \({{\text{M}}^{{\text{2 + }}}}\), form the complexes \({\left[ {{\text{M}}{{\left( {{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}} \right)}_{\text{6}}}} \right]^{{\text{2 + }}}}{\text{,}}{\left[ {{\text{M(en}}{{\text{)}}_{\text{3}}}} \right]^{{\text{2 + }}}}\) and \({\left[ {{\text{MB}}{{\text{r}}_{\text{6}}}} \right]^{{\text{4 - }}}}\) Colour of these complexes may be:
321794 An ion \({{\text{M}}^{{\text{2 + }}}}\), form the complexes \({\left[ {{\text{M}}{{\left( {{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}} \right)}_{\text{6}}}} \right]^{{\text{2 + }}}}{\text{,}}{\left[ {{\text{M(en}}{{\text{)}}_{\text{3}}}} \right]^{{\text{2 + }}}}\) and \({\left[ {{\text{MB}}{{\text{r}}_{\text{6}}}} \right]^{{\text{4 - }}}}\) Colour of these complexes may be:
321794 An ion \({{\text{M}}^{{\text{2 + }}}}\), form the complexes \({\left[ {{\text{M}}{{\left( {{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}} \right)}_{\text{6}}}} \right]^{{\text{2 + }}}}{\text{,}}{\left[ {{\text{M(en}}{{\text{)}}_{\text{3}}}} \right]^{{\text{2 + }}}}\) and \({\left[ {{\text{MB}}{{\text{r}}_{\text{6}}}} \right]^{{\text{4 - }}}}\) Colour of these complexes may be:
321794 An ion \({{\text{M}}^{{\text{2 + }}}}\), form the complexes \({\left[ {{\text{M}}{{\left( {{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}} \right)}_{\text{6}}}} \right]^{{\text{2 + }}}}{\text{,}}{\left[ {{\text{M(en}}{{\text{)}}_{\text{3}}}} \right]^{{\text{2 + }}}}\) and \({\left[ {{\text{MB}}{{\text{r}}_{\text{6}}}} \right]^{{\text{4 - }}}}\) Colour of these complexes may be: