358308
A cubical Gaussian surface has side of length \(a = 10\;cm\). Electric field lines are parallel to \(x - \)axis as shown. The magnitudes of electric fields through surfaces \(A B C D\) and \(E F G H\) are \(6 k N C^{-1}\) and \(9 k N C^{-1}\) respectively. Then the total charge enclosed by the cube is \(\left[ {{\rm{Take}}\,\,{\varepsilon _0} = 9 \times {{10}^{ - 12}}F{m^{ - 1}}} \right]\)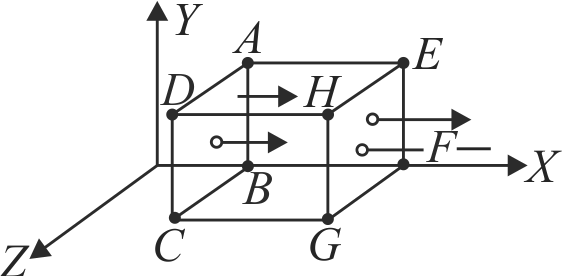
358308
A cubical Gaussian surface has side of length \(a = 10\;cm\). Electric field lines are parallel to \(x - \)axis as shown. The magnitudes of electric fields through surfaces \(A B C D\) and \(E F G H\) are \(6 k N C^{-1}\) and \(9 k N C^{-1}\) respectively. Then the total charge enclosed by the cube is \(\left[ {{\rm{Take}}\,\,{\varepsilon _0} = 9 \times {{10}^{ - 12}}F{m^{ - 1}}} \right]\)
358308
A cubical Gaussian surface has side of length \(a = 10\;cm\). Electric field lines are parallel to \(x - \)axis as shown. The magnitudes of electric fields through surfaces \(A B C D\) and \(E F G H\) are \(6 k N C^{-1}\) and \(9 k N C^{-1}\) respectively. Then the total charge enclosed by the cube is \(\left[ {{\rm{Take}}\,\,{\varepsilon _0} = 9 \times {{10}^{ - 12}}F{m^{ - 1}}} \right]\)
358308
A cubical Gaussian surface has side of length \(a = 10\;cm\). Electric field lines are parallel to \(x - \)axis as shown. The magnitudes of electric fields through surfaces \(A B C D\) and \(E F G H\) are \(6 k N C^{-1}\) and \(9 k N C^{-1}\) respectively. Then the total charge enclosed by the cube is \(\left[ {{\rm{Take}}\,\,{\varepsilon _0} = 9 \times {{10}^{ - 12}}F{m^{ - 1}}} \right]\)
