357246
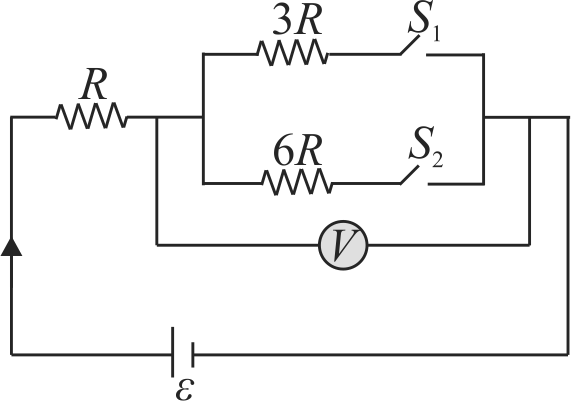
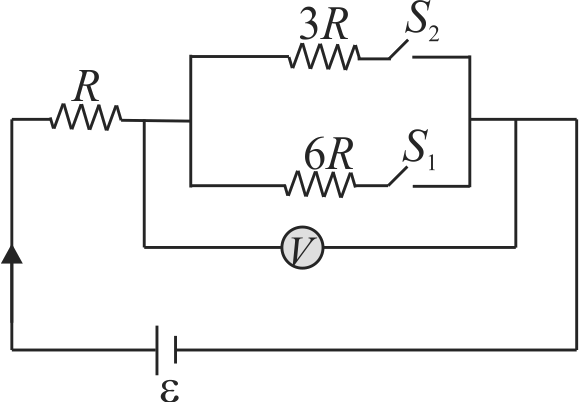
A voltmeter connected in series with a resistance \({R_{1}}\) to a circuit indicates a voltage \({V_{1}=198 {~V}}\). When a series resistor \({R_{2}=2 R_{1}}\) is used, the voltmeter indicates a voltage \({V_{2}=180 {~V}}\). If the resistance of the voltmeter is \({R_{V}=900 \Omega}\), find the applied voltage across \({A}\) and \({B}\).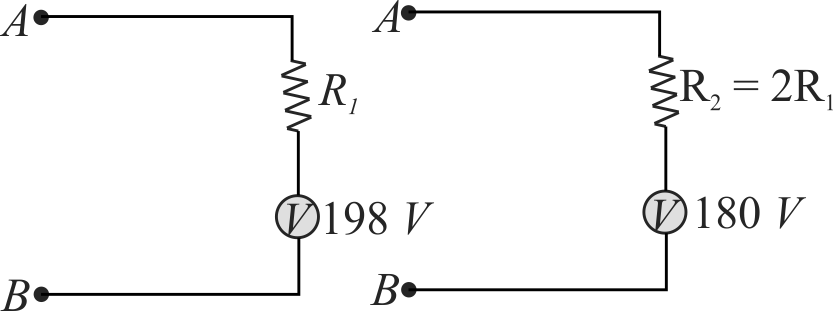
357246
A voltmeter connected in series with a resistance \({R_{1}}\) to a circuit indicates a voltage \({V_{1}=198 {~V}}\). When a series resistor \({R_{2}=2 R_{1}}\) is used, the voltmeter indicates a voltage \({V_{2}=180 {~V}}\). If the resistance of the voltmeter is \({R_{V}=900 \Omega}\), find the applied voltage across \({A}\) and \({B}\).
357246
A voltmeter connected in series with a resistance \({R_{1}}\) to a circuit indicates a voltage \({V_{1}=198 {~V}}\). When a series resistor \({R_{2}=2 R_{1}}\) is used, the voltmeter indicates a voltage \({V_{2}=180 {~V}}\). If the resistance of the voltmeter is \({R_{V}=900 \Omega}\), find the applied voltage across \({A}\) and \({B}\).
357246
A voltmeter connected in series with a resistance \({R_{1}}\) to a circuit indicates a voltage \({V_{1}=198 {~V}}\). When a series resistor \({R_{2}=2 R_{1}}\) is used, the voltmeter indicates a voltage \({V_{2}=180 {~V}}\). If the resistance of the voltmeter is \({R_{V}=900 \Omega}\), find the applied voltage across \({A}\) and \({B}\).