282046
If the reflected image formed is magnified and virtual, then the mirror system is
1 concave only
2 convex only
3 plane
4 concave or convex
(e) convex or plane
Explanation:
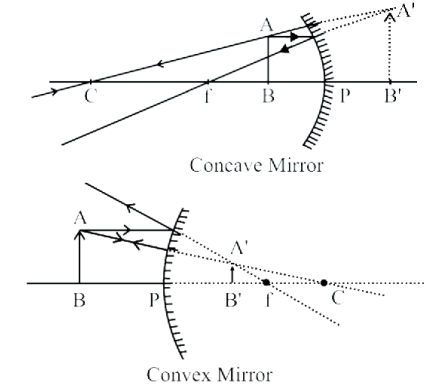
A: Magnified and virtual image are only formed by concave mirror.
Virtual erect and diminished size image are formed by convex mirror.
Concave Mirror
Kerala CEE - 2010
Ray Optics
282047
A square wire of side $1 \mathrm{~cm}$ is placed perpendicular to the principal axis of a concave mirror of focal length $15 \mathrm{~cm}$ at a distance of 20 $\mathrm{cm}$. The area enclosed by the image of the wire is
1 $4 \mathrm{~cm}^2$
2 $6 \mathrm{~cm}^2$
3 $2 \mathrm{~cm}^2$
4 $8 \mathrm{~cm}^2$
(e) $9 \mathrm{~cm}^2$
Explanation:
E : Given, focal length (f) $=-15 \mathrm{~cm}$
Object distance $(\mathrm{u})=-20 \mathrm{~cm}$
Height of object $\left(\mathrm{h}_0\right)=1 \mathrm{~cm}$
From mirror formula,
$\begin{aligned}
\frac{1}{\mathrm{f}}=\frac{1}{\mathrm{u}}+\frac{1}{\mathrm{v}} \\
-\frac{1}{15}=-\frac{1}{20}+\frac{1}{\mathrm{v}} \\
\frac{1}{\mathrm{v}}=\frac{1}{20}-\frac{1}{15} \\
\frac{1}{\mathrm{v}}=\frac{3-4}{60} \\
\mathrm{v}=-60 \mathrm{~cm}
\end{aligned}$
Magnification $(\mathrm{m})=\frac{\mathrm{h}_{\mathrm{i}}}{\mathrm{h}_0}=-\frac{\mathrm{v}}{\mathrm{u}}$
$\begin{gathered}
\frac{\mathrm{h}_{\mathrm{i}}}{1}=-\frac{(-60)}{(-20)} \\
\mathrm{h}_{\mathrm{i}}=-3 \mathrm{~cm}
\end{gathered}$
Hence, area of image $\left(\mathrm{A}_{\mathrm{i}}\right)=\left(\mathrm{h}_{\mathrm{i}}\right)^2$
$=(-3)^2=9 \mathrm{~cm}^2$
Kerala CEE - 2009
Ray Optics
282048
The magnification of the image when an object is placed at a distance $x$ from the principal focus of a mirror of focal length $f$ is:
NEET Test Series from KOTA - 10 Papers In MS WORD
WhatsApp Here
Ray Optics
282046
If the reflected image formed is magnified and virtual, then the mirror system is
1 concave only
2 convex only
3 plane
4 concave or convex
(e) convex or plane
Explanation:
A: Magnified and virtual image are only formed by concave mirror.
Virtual erect and diminished size image are formed by convex mirror.
Concave Mirror

Kerala CEE - 2010
Ray Optics
282047
A square wire of side $1 \mathrm{~cm}$ is placed perpendicular to the principal axis of a concave mirror of focal length $15 \mathrm{~cm}$ at a distance of 20 $\mathrm{cm}$. The area enclosed by the image of the wire is
1 $4 \mathrm{~cm}^2$
2 $6 \mathrm{~cm}^2$
3 $2 \mathrm{~cm}^2$
4 $8 \mathrm{~cm}^2$
(e) $9 \mathrm{~cm}^2$
Explanation:
E : Given, focal length (f) $=-15 \mathrm{~cm}$
Object distance $(\mathrm{u})=-20 \mathrm{~cm}$
Height of object $\left(\mathrm{h}_0\right)=1 \mathrm{~cm}$
From mirror formula,
$\begin{aligned}
\frac{1}{\mathrm{f}}=\frac{1}{\mathrm{u}}+\frac{1}{\mathrm{v}} \\
-\frac{1}{15}=-\frac{1}{20}+\frac{1}{\mathrm{v}} \\
\frac{1}{\mathrm{v}}=\frac{1}{20}-\frac{1}{15} \\
\frac{1}{\mathrm{v}}=\frac{3-4}{60} \\
\mathrm{v}=-60 \mathrm{~cm}
\end{aligned}$
Magnification $(\mathrm{m})=\frac{\mathrm{h}_{\mathrm{i}}}{\mathrm{h}_0}=-\frac{\mathrm{v}}{\mathrm{u}}$
$\begin{gathered}
\frac{\mathrm{h}_{\mathrm{i}}}{1}=-\frac{(-60)}{(-20)} \\
\mathrm{h}_{\mathrm{i}}=-3 \mathrm{~cm}
\end{gathered}$
Hence, area of image $\left(\mathrm{A}_{\mathrm{i}}\right)=\left(\mathrm{h}_{\mathrm{i}}\right)^2$
$=(-3)^2=9 \mathrm{~cm}^2$
Kerala CEE - 2009
Ray Optics
282048
The magnification of the image when an object is placed at a distance $x$ from the principal focus of a mirror of focal length $f$ is:
282046
If the reflected image formed is magnified and virtual, then the mirror system is
1 concave only
2 convex only
3 plane
4 concave or convex
(e) convex or plane
Explanation:
A: Magnified and virtual image are only formed by concave mirror.
Virtual erect and diminished size image are formed by convex mirror.
Concave Mirror

Kerala CEE - 2010
Ray Optics
282047
A square wire of side $1 \mathrm{~cm}$ is placed perpendicular to the principal axis of a concave mirror of focal length $15 \mathrm{~cm}$ at a distance of 20 $\mathrm{cm}$. The area enclosed by the image of the wire is
1 $4 \mathrm{~cm}^2$
2 $6 \mathrm{~cm}^2$
3 $2 \mathrm{~cm}^2$
4 $8 \mathrm{~cm}^2$
(e) $9 \mathrm{~cm}^2$
Explanation:
E : Given, focal length (f) $=-15 \mathrm{~cm}$
Object distance $(\mathrm{u})=-20 \mathrm{~cm}$
Height of object $\left(\mathrm{h}_0\right)=1 \mathrm{~cm}$
From mirror formula,
$\begin{aligned}
\frac{1}{\mathrm{f}}=\frac{1}{\mathrm{u}}+\frac{1}{\mathrm{v}} \\
-\frac{1}{15}=-\frac{1}{20}+\frac{1}{\mathrm{v}} \\
\frac{1}{\mathrm{v}}=\frac{1}{20}-\frac{1}{15} \\
\frac{1}{\mathrm{v}}=\frac{3-4}{60} \\
\mathrm{v}=-60 \mathrm{~cm}
\end{aligned}$
Magnification $(\mathrm{m})=\frac{\mathrm{h}_{\mathrm{i}}}{\mathrm{h}_0}=-\frac{\mathrm{v}}{\mathrm{u}}$
$\begin{gathered}
\frac{\mathrm{h}_{\mathrm{i}}}{1}=-\frac{(-60)}{(-20)} \\
\mathrm{h}_{\mathrm{i}}=-3 \mathrm{~cm}
\end{gathered}$
Hence, area of image $\left(\mathrm{A}_{\mathrm{i}}\right)=\left(\mathrm{h}_{\mathrm{i}}\right)^2$
$=(-3)^2=9 \mathrm{~cm}^2$
Kerala CEE - 2009
Ray Optics
282048
The magnification of the image when an object is placed at a distance $x$ from the principal focus of a mirror of focal length $f$ is:
282046
If the reflected image formed is magnified and virtual, then the mirror system is
1 concave only
2 convex only
3 plane
4 concave or convex
(e) convex or plane
Explanation:
A: Magnified and virtual image are only formed by concave mirror.
Virtual erect and diminished size image are formed by convex mirror.
Concave Mirror

Kerala CEE - 2010
Ray Optics
282047
A square wire of side $1 \mathrm{~cm}$ is placed perpendicular to the principal axis of a concave mirror of focal length $15 \mathrm{~cm}$ at a distance of 20 $\mathrm{cm}$. The area enclosed by the image of the wire is
1 $4 \mathrm{~cm}^2$
2 $6 \mathrm{~cm}^2$
3 $2 \mathrm{~cm}^2$
4 $8 \mathrm{~cm}^2$
(e) $9 \mathrm{~cm}^2$
Explanation:
E : Given, focal length (f) $=-15 \mathrm{~cm}$
Object distance $(\mathrm{u})=-20 \mathrm{~cm}$
Height of object $\left(\mathrm{h}_0\right)=1 \mathrm{~cm}$
From mirror formula,
$\begin{aligned}
\frac{1}{\mathrm{f}}=\frac{1}{\mathrm{u}}+\frac{1}{\mathrm{v}} \\
-\frac{1}{15}=-\frac{1}{20}+\frac{1}{\mathrm{v}} \\
\frac{1}{\mathrm{v}}=\frac{1}{20}-\frac{1}{15} \\
\frac{1}{\mathrm{v}}=\frac{3-4}{60} \\
\mathrm{v}=-60 \mathrm{~cm}
\end{aligned}$
Magnification $(\mathrm{m})=\frac{\mathrm{h}_{\mathrm{i}}}{\mathrm{h}_0}=-\frac{\mathrm{v}}{\mathrm{u}}$
$\begin{gathered}
\frac{\mathrm{h}_{\mathrm{i}}}{1}=-\frac{(-60)}{(-20)} \\
\mathrm{h}_{\mathrm{i}}=-3 \mathrm{~cm}
\end{gathered}$
Hence, area of image $\left(\mathrm{A}_{\mathrm{i}}\right)=\left(\mathrm{h}_{\mathrm{i}}\right)^2$
$=(-3)^2=9 \mathrm{~cm}^2$
Kerala CEE - 2009
Ray Optics
282048
The magnification of the image when an object is placed at a distance $x$ from the principal focus of a mirror of focal length $f$ is: