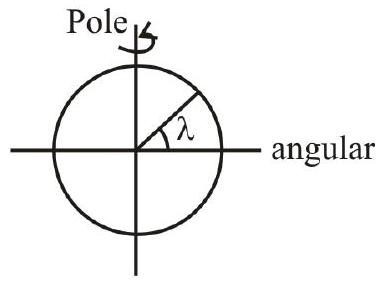
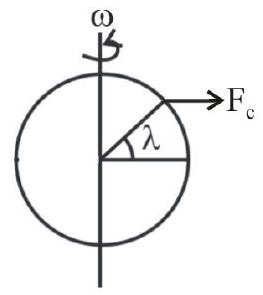
138331 The earth is assumed to be a sphere of radius (R) rotating about its axis with an angular speed $\omega$. If the effective acceleration due to gravity at a certain latitude $\lambda$ is $g_{p}-\frac{3}{4} \omega^{2} R$, where $g_{p}$ is the acceleration due to gravity at the poles, then the value of $\lambda$ is
138331 The earth is assumed to be a sphere of radius (R) rotating about its axis with an angular speed $\omega$. If the effective acceleration due to gravity at a certain latitude $\lambda$ is $g_{p}-\frac{3}{4} \omega^{2} R$, where $g_{p}$ is the acceleration due to gravity at the poles, then the value of $\lambda$ is
138331 The earth is assumed to be a sphere of radius (R) rotating about its axis with an angular speed $\omega$. If the effective acceleration due to gravity at a certain latitude $\lambda$ is $g_{p}-\frac{3}{4} \omega^{2} R$, where $g_{p}$ is the acceleration due to gravity at the poles, then the value of $\lambda$ is
138331 The earth is assumed to be a sphere of radius (R) rotating about its axis with an angular speed $\omega$. If the effective acceleration due to gravity at a certain latitude $\lambda$ is $g_{p}-\frac{3}{4} \omega^{2} R$, where $g_{p}$ is the acceleration due to gravity at the poles, then the value of $\lambda$ is