138260
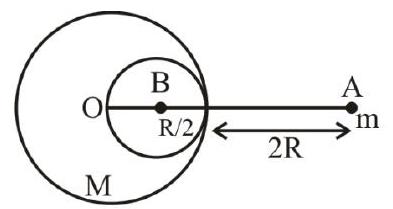
A solid sphere of radius $R$ gravitationally attracts a particle of mass $m$ at a distance $3 R$ from its centre such that the force is $F_{1}$. Now a spherical cavity of radius $\frac{R}{2}$ is extracted (as shown in the figure below) from the sphere and the force becomes $F_{2}$. The value of $\frac{F_{1}}{F_{2}}$ is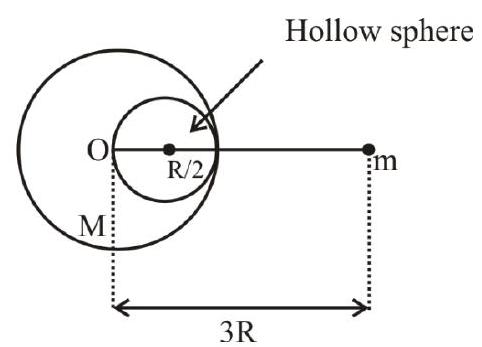
138260
A solid sphere of radius $R$ gravitationally attracts a particle of mass $m$ at a distance $3 R$ from its centre such that the force is $F_{1}$. Now a spherical cavity of radius $\frac{R}{2}$ is extracted (as shown in the figure below) from the sphere and the force becomes $F_{2}$. The value of $\frac{F_{1}}{F_{2}}$ is
138260
A solid sphere of radius $R$ gravitationally attracts a particle of mass $m$ at a distance $3 R$ from its centre such that the force is $F_{1}$. Now a spherical cavity of radius $\frac{R}{2}$ is extracted (as shown in the figure below) from the sphere and the force becomes $F_{2}$. The value of $\frac{F_{1}}{F_{2}}$ is
138260
A solid sphere of radius $R$ gravitationally attracts a particle of mass $m$ at a distance $3 R$ from its centre such that the force is $F_{1}$. Now a spherical cavity of radius $\frac{R}{2}$ is extracted (as shown in the figure below) from the sphere and the force becomes $F_{2}$. The value of $\frac{F_{1}}{F_{2}}$ is